- OEM
- Catalyst technologies
Catalyst Technologies
Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC)
The primary function of the DOC in a Diesel ATS is to ensure sufficient oxidation of CO and THC and to convert between 30 and 60% of the NO in the exhaust to NO2.
The Dinex DOC technologies are based on a high thermal stable wash coat formulation with excellent CO and THC light-off characteristics and high NO2 formation. The typical CO and THC conversion levels are above 95%.
A high level of NO2 generated on the DOC ensures in combination with a sufficient NOx/soot ratio a good passive soot oxidation on the DPF in normal operation conditions. This CRT effect (continuous regenerated trap) ensures long regeneration intervals for the DPF which saves fuel.
Excellent THC light-off characteristics support and offer flexibility in designing active DPF regeneration strategies through external measures like HC dosing. The PGM loading and the Pt:Pd ratio can be modulated based on DPF regeneration strategies and requirements.
A high NO2 formation at temperature of 200 – 250°C is also helpful for the DeNOx function of any possible SCR system positioned after the DPF in the ATS.
The catalyst coating can be done on metallic as well as ceramic based substrates.

Diesel Particulate Filter Coating (C-DPF)
The primary function of the DPF in a Diesel ATS is to trap and oxidize the soot particulates in the exhaust. The DPFs are typically coated with a low PGM content wash coat and are known as catalyzed DPFs (cDPF). The coating ensures further oxidation of NO to NO2 at the DPF surface which supports the passive regeneration and it also works as an oxidation catalyst for any CO or THC slip from the DOC during active regeneration.
Dinex DPF coating technologies are based on a high thermal stable wash coat formulation with excellent NO2 formation characteristics. The PGM loading can be modulated based on the application and the typical duty cycle requirements.
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
The primary function of the SCR catalyst in a Diesel ATS is to convert harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx = NO + NO2) in the exhaust gas to nitrogen and water. The SCR reaction takes place at the catalyst surface in the presence of NH3 which is generated from AdBlue®/DEF (solution of 30% of Urea in water) upfront the SCR catalyst.
Dinex has a variety of SCR catalyst technologies that can be selected based on specific application conditions and ATS temperature levels. Typically, titanium-vanadium based technologies are suitable for applications, where the exhaust gas temperature is not exceeding 550°C level. The Cu-SCR technology is designed for high DeNOx functionality at low temperatures and the Fe-SCR technology is suitable for conditions where the exhaust temperatures exceed 600°C.
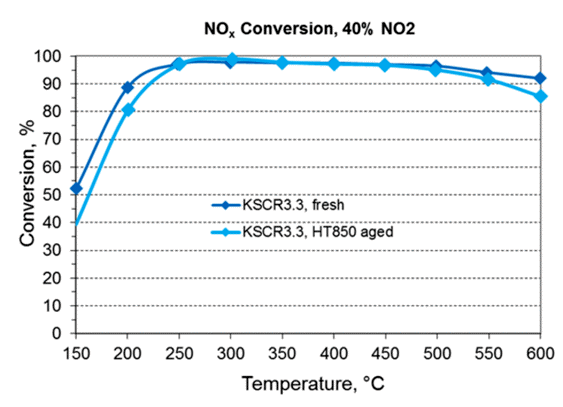
Advanced emissions regulations like EuroVI / EPA10 / China N6 / Bharat S6 need more than 95% NOx conversion levels and the Dinex Cu-SCR technology achieves conversion levels well above this limit.
This SCR technology is typically characterized by high NOx conversion activity in a wide temperature window with very low NH3 oxidation at high temperatures which ensures optimal AdBlue®/DEF utilization.

Dinex V-SCR
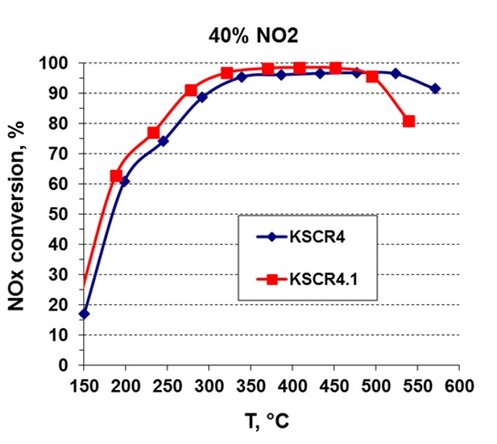
Dinex Cu-SCR
SCR on DPF (SCR-DPF)
The SCR on DPF technology integrates the SCR function into the particle filter (DPF) which enables compact ATS systems, a fast heat up of the first SCR catalyst in the exhaust stream and by this the possibility of an AdBlue dosing at lower temperatures. This technology has gained relevance in many applications in the off-road segment, where especially space restrictions are a key challenge.
The Dinex SCR on DPF coating technology is based on Cu- and Fe-SCR based wash coats and offer excellent NOx conversion levels. They typically offer a 20% reduction in the overall SCR catalyst volume.

Cu-Ze coating on SiC substrate
Three-Way Catalyst (TWC)
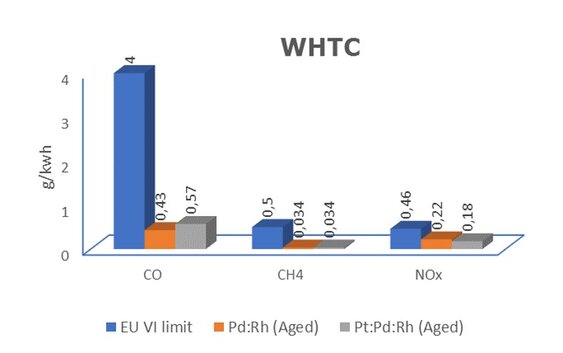
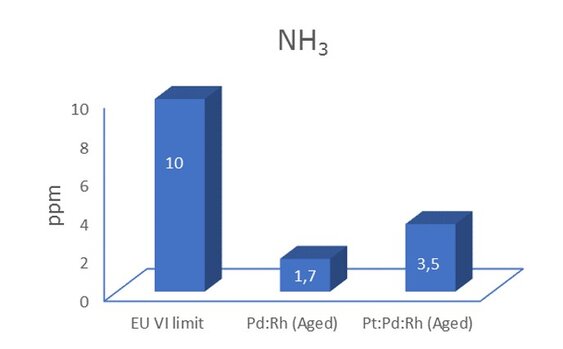
The primary function of a three-way catalyst (TWC) in a CNG/LNG ATS is to convert and minimize emissions of harmful species like THC, CO, and NOx below the regulatory limits.
The TWC by Dinex is a Pd-Rh-based technology with a high surface area wash coat formulation that contains high oxygen storage capacity (OSC) materials, stabilizers, and promoters with optimized active (PGM) metal content. The TWC product portfolio covers both bimetallic (Pd:Rh) and trimetallic ( Pt:Pd:Rh) options both with high surface area wash coat, high oxygen storage capacity (OSC) material, etc.
Customized PGM loadings and ratios are used to tailor our technology to the application for the best possible compromise of performance and cost.
The coating can be applied to metallic as well as ceramic substrates with excellent adhesion

Methane Oxidation Catalyst (MOC)
The Dinex methane oxidation catalyst for lean-burn CNG engines is based on a high surface area wash coat with Sulphur resistant components. It is suitable for mobile or stationary applications. The highly dispersed PGM nanoparticles with Pt-Pd or Pt only formulation suit the emission demands according to the requirements.
It is available on metallic as well as on ceramic substrates with excellent adhesion.
